
Introduzione

Menu
 Introduzione |
RESOCONTO IN LINGUA INGLESE |
 Menu |
 Volcanoes are closely
associated with tectonic activity. Most of them occur on either the overriding
or the diverging margins of the enormous lithospheric plates that make up the
Earth 's surface.
Volcanoes are closely
associated with tectonic activity. Most of them occur on either the overriding
or the diverging margins of the enormous lithospheric plates that make up the
Earth 's surface.
There are six major types of eruptions: The ICELANDIC type, the HAWAIIAN type, the STROMBOLIAN type, the VULCANIC type, the PELEIAN type and the PLINIAN type.
The Plinian type is an intensely violent kind of volcanic eruption exemplified by the outburst of Mt. Vesuvius in AD 79 that killed the famous Pliny the Elder, from whom the name is taken.
The uprushing gases and volcanic fragments appear like a gigantic rocket blast directed vertically upward. Plinian eruption clouds can rise into the stratosphere and are sometimes sustained for several hours.
In AD 79 the great eruption of Vesuvius buried the seaside towns of Pompeii, Herculaneum, and Stabiae, engulfing also many villas confidently constructed on the slopes of a mountain that had not erupted for more than seven centuries. A contemporary account of this event remains to us in two letters addressed to the historian Tacitus by Pliny the Younger, who describes the doomed attempt of his uncle, the elder Pliny, to rescue survivors by sea.
The elder Pliny perished at Stabiae, near the villa of his friend Pomponianus.
ELENCO DEI VOCABOLI IN ORDINE ALFABETICO
| Alternate operations of fire and water = Azioni alternate di fuoco e acqua | grumbles = brontola |
| ashes =ceneri | height = altezza |
| a river of red hot and liquid metal = un fiume di metallo rosso e liquefatto | grumblings = brontolii |
| astonishing artificial fireworks =fuochi d'artificio spettacolari | hill = collina |
| atmosphere = atmosfera | impregnated with = impregnato di |
| bad weather = cattivo tempo | interesting spot = luogo interessante |
| bed = letto | lava = lava |
| black smoke = fumo nero | materials = materiali |
| bowels of the volcan = viscere del vulcano | matter = materiale |
| broke out = esplose | mountain = montagna |
|
changes = mutamenti |
mouth = bocca |
| cinders = ceneri | pumice stones = pietre pomici |
| column = colonna | representations = rappresentazioni |
| crevices = fessure | rounded pebbles = ciottoli arrotondati |
| damage = danno | ruins = rovine |
| destroy = distruzione | service = utilità |
| dissipation = dispersione | shape = forma |
| detrimental = nocivo | shower of stones = pioggia di pietre |
| earthquake = terremoto | snow = neve |
| emission = emissione | smoke = fumo |
| explosions = esplosioni | stratum = strato |
| eruption = eruzione | sulphur = sulfureo |
| fermentation = fermentazione | thrown up = scagliato |
| fell in = ricadde | top = cima |
| feet = piedi ; un piede =cm.30,479 | tufa = tufo |
| fertility = fertilità |
vegetation = vegetazione |
| fragments = frammenti | violent explosions = esplosioni violente |
| flame =fiamma | volcan = vulcano |
| girandoles of red hot stones = girandole di pietre rosse infuocate | volcanic matter = materiale vulcanico |
LE ROCCE
(clicca sulle immagini)
Vari sono i fenomeni di vulcanesimo secondario :
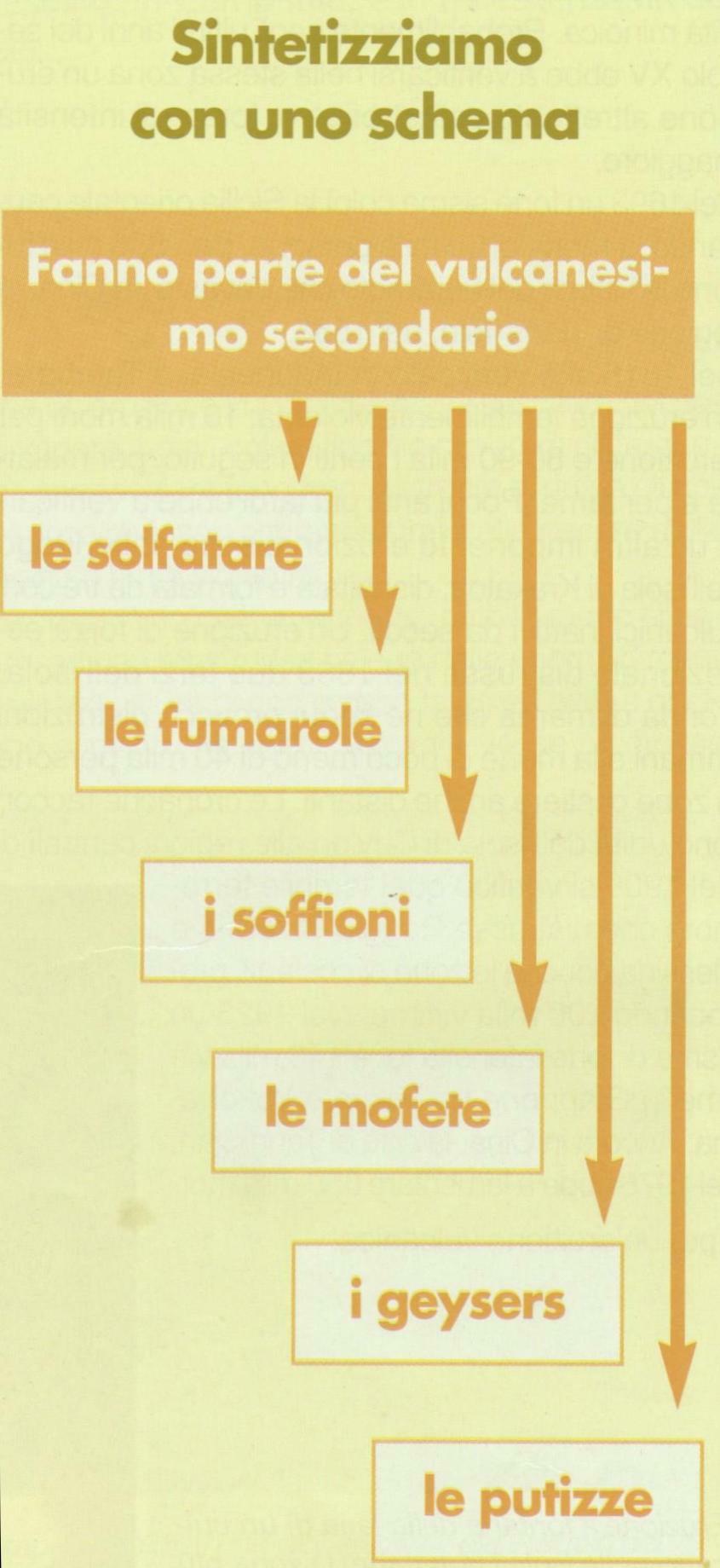
(clicca sulle parole)
|
|
MENU |
|